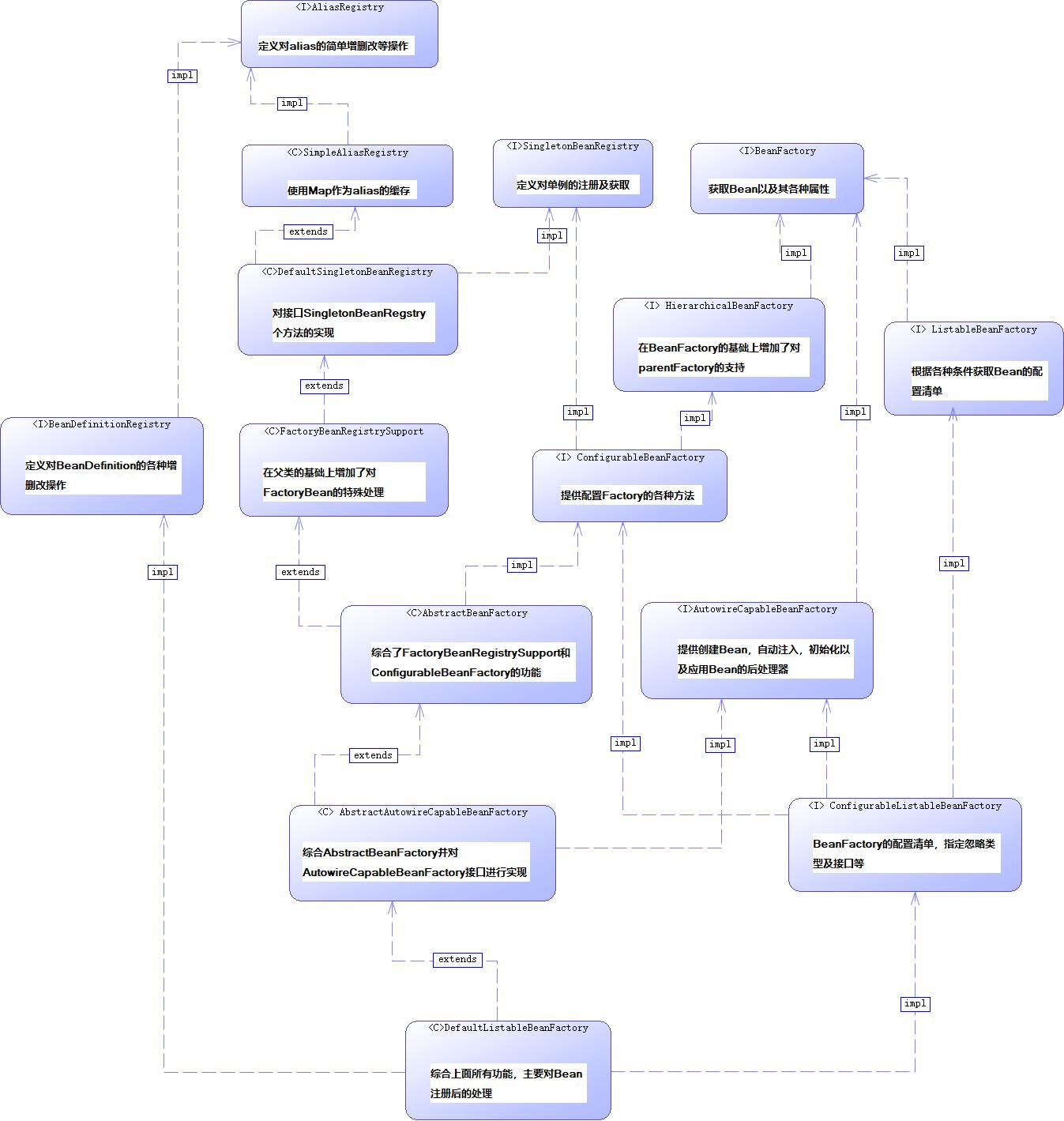
XmlBeanFactory继承自DefaultListableBeanFactory,而DefaultListableBeanFactory是整个bean加载的核心部分,是Spring注册及加载bean的默认实现,对于XmlBeanFactory,使用了自定义的XML读取器XmlBeanDefinitionReader,实现了个性化的BeanDefinitionReader读取。
前言 作为Spring源码的第一篇,首先先简单介绍Spring的整体架构
Core Container(核心容器)
Data Access / Integration
WEB
AOP
Bean容器 bean是Spring中最核心的东西,因为Spring就像是个大水桶,而bean就像是容器中的水,水桶脱离了水也就没什么作用了。在这里我讲解一下利用读取XML文件进行Bean容器的基本实现。
核心类一: DefaultListableBeanFactory
XmlBeanFactory继承自DefaultListableBeanFactory,而DefaultListableBeanFactory是整个bean加载的核心部分,是Spring注册及加载bean的默认实现,对于XmlBeanFactory,使用了自定义的XML读取器XmlBeanDefinitionReader,实现了个性化的BeanDefinitionReader读取。
singletonBeanRegistry: 定义对单例的注册及获取。
BeanFactory: 定义获取bean及bean的各种属性。
DefaultSingletonBeanRegistry: 对接口SingletonBeanRegistry各函数的实现。
HierarchicalBeanFactory: 继承BeanFactory,增加了对parentFactory的支持。
BeanDefinitionRegistry: 定义对BeanDefinition的各种增删改操作。
ConfigurableBeanFactory: 提供配置Factory的各种方法。
ListableBeanFactory: 根据各种 条件获取bean的配置清单。
AutowireCapableBeanFactory: 提供创建bean、自动注入、初始化以及应用bean的后处理器。
XmlBeanFactory对DefaultListableBeanFactory类进行了扩展,主要用于从XML文档中读取BeanDefinition,以及注册及获取bean。
核心类二: XmlBeanDefinitionReader
ResourceLoader: 定义资源加载器,主要应用于根据给定的资源文件地址返回对应的Resource.
BeanDefinitionReader: 主要定义资源文件读取并转换为BeanDefinition的各个功能。
BeanDefinitionDocumentReader: 定义读取Document并注册BeanDefinition.容器的基础XmlBeanFactory 当前获取创建beanFactory的代码如下
BeanFactory bf = new XmlBeanFactory(new ClassPathResource(“beanFactoryTest.xml”))
首先,读取配置文件,用ClassPathResource进行封装。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 public interface InputStreamSource InputStream getInputStream () throws IOException ; } public interface Resource extends InputStreamSource boolean exists () boolean isReadable () boolean isOpen () URL getURL () throws IOException ; URI getURI () throws IOException ; File getFile () throws IOException ; long contentLength () throws IOException long lastModified () throws IOException Resource createRelative (String relativePath) throws IOException ; String getFilename () ; String getDescription () ; }
对不同来源的资源文件都有相应的Resource实现:
文件 FileSystemResource
Classpath资源 ClassPathResource
URL资源 UrlResource
InputStream资源 InputStreamResource
Byte数组 ByteArrayResource
XmlBeanFactory loadBeanDefinitions(Resource) –> 进行资源加载
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 private final XmlBeanDefinitionReader reader = new XmlBeanDefinitionReader(this );public XmlBeanFactory (Resource resource) throws BeansException this (resource, null ); } public XmlBeanFactory (Resource resource, BeanFactory parentBeanFactory) throws BeansException super (parentBeanFactory); this .reader.loadBeanDefinitions(resource); } @Override public int loadBeanDefinitions (Resource resource) throws BeanDefinitionStoreException return loadBeanDefinitions(new EncodedResource(resource)); }
从上面可知,主要加载Bean的步骤
封装资源文件,当进入XmlBeanDefinitionReader后首先对参数Resource使用EncodedResource类进行封装。
获取输入流。从Resource中获取对应的InputStream并构造InputSource
通过构造的InputSource实例和Resource实例继续调用函数doLoadBeanDefinitions.
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 public int loadBeanDefinitions (EncodedResource encodedResource) throws BeanDefinitionStoreException Assert.notNull(encodedResource, "EncodedResource must not be null" ); if (logger.isInfoEnabled()) { logger.info("Loading XML bean definitions from " + encodedResource); } Set<EncodedResource> currentResources = this .resourcesCurrentlyBeingLoaded.get(); if (currentResources == null ) { currentResources = new HashSet<>(4 ); this .resourcesCurrentlyBeingLoaded.set(currentResources); } if (!currentResources.add(encodedResource)) { throw new BeanDefinitionStoreException( "Detected cyclic loading of " + encodedResource + " - check your import definitions!" ); } try { InputStream inputStream = encodedResource.getResource().getInputStream(); try { InputSource inputSource = new InputSource(inputStream); if (encodedResource.getEncoding() != null ) { inputSource.setEncoding(encodedResource.getEncoding()); } return doLoadBeanDefinitions(inputSource, encodedResource.getResource()); } finally { inputStream.close(); } } catch (IOException ex) { throw new BeanDefinitionStoreException( "IOException parsing XML document from " + encodedResource.getResource(), ex); } finally { currentResources.remove(encodedResource); if (currentResources.isEmpty()) { this .resourcesCurrentlyBeingLoaded.remove(); } } }
核心代码doLoadBeanDefinitions
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 protected int doLoadBeanDefinitions (InputSource inputSource, Resource resource) throws BeanDefinitionStoreException { try { Document doc = doLoadDocument(inputSource, resource); return registerBeanDefinitions(doc, resource); } catch (BeanDefinitionStoreException ex) { throw ex; } catch (SAXParseException ex) { throw new XmlBeanDefinitionStoreException(resource.getDescription(), "Line " + ex.getLineNumber() + " in XML document from " + resource + " is invalid" , ex); } catch (SAXException ex) { throw new XmlBeanDefinitionStoreException(resource.getDescription(), "XML document from " + resource + " is invalid" , ex); } catch (ParserConfigurationException ex) { throw new BeanDefinitionStoreException(resource.getDescription(), "Parser configuration exception parsing XML from " + resource, ex); } catch (IOException ex) { throw new BeanDefinitionStoreException(resource.getDescription(), "IOException parsing XML document from " + resource, ex); } catch (Throwable ex) { throw new BeanDefinitionStoreException(resource.getDescription(), "Unexpected exception parsing XML document from " + resource, ex); } }
主要步骤:
获取对XML文件的检验方式
加载XML文件,并得到对应的Document.
根据返回的Document注册Bean信息。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 public int registerBeanDefinitions (Document doc, Resource resource) throws BeanDefinitionStoreException BeanDefinitionDocumentReader documentReader = createBeanDefinitionDocumentReader(); int countBefore = getRegistry().getBeanDefinitionCount(); documentReader.registerBeanDefinitions(doc, createReaderContext(resource)); return getRegistry().getBeanDefinitionCount() - countBefore; }
之后调用DefaultBeanDefinitionDocumentReader的registerBeanDefinitions()
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 @Override public void registerBeanDefinitions (Document doc, XmlReaderContext readerContext) this .readerContext = readerContext; logger.debug("Loading bean definitions" ); Element root = doc.getDocumentElement(); doRegisterBeanDefinitions(root); }
注意,下面是最最最核心的代码
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 protected void doRegisterBeanDefinitions (Element root) BeanDefinitionParserDelegate parent = this .delegate; this .delegate = createDelegate(getReaderContext(), root, parent); if (this .delegate.isDefaultNamespace(root)) { String profileSpec = root.getAttribute(PROFILE_ATTRIBUTE); if (StringUtils.hasText(profileSpec)) { String[] specifiedProfiles = StringUtils.tokenizeToStringArray( profileSpec, BeanDefinitionParserDelegate.MULTI_VALUE_ATTRIBUTE_DELIMITERS); if (!getReaderContext().getEnvironment().acceptsProfiles(specifiedProfiles)) { if (logger.isInfoEnabled()) { logger.info("Skipped XML bean definition file due to specified profiles [" + profileSpec + "] not matching: " + getReaderContext().getResource()); } return ; } } } preProcessXml(root); parseBeanDefinitions(root, this .delegate); postProcessXml(root); this .delegate = parent; }
preProcessXml和postProcessXml是两个抽象方法,是为了子类而设计的,这是设计模式的模板方法模式,如果子类想在Bean解析前后做一些处理,那么只需处理这两个方法即可。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 protected void parseBeanDefinitions (Element root, BeanDefinitionParserDelegate delegate) if (delegate.isDefaultNamespace(root)) { NodeList nl = root.getChildNodes(); for (int i = 0 ; i < nl.getLength(); i++) { Node node = nl.item(i); if (node instanceof Element) { Element ele = (Element) node; if (delegate.isDefaultNamespace(ele)) { parseDefaultElement(ele, delegate); } else { delegate.parseCustomElement(ele); } } } } else { delegate.parseCustomElement(root); } }
如果采用Spring默认的配置,Spring当然知道怎么做,但是如果是自定义的,那么就需要用户实现一些接口及配置了。具体的元素解析在下一篇编写。