Dubbo是SOA(面向服务架构)服务治理方案的核心框架。用于分布式调用,其重点在于分布式的治理。
从今天开始,将会逐步介绍关于DUbbo的有关知识。首先先简单介绍一下DUbbo的整体概述。
概述 Dubbo是SOA(面向服务架构)服务治理方案的核心框架。用于分布式调用,其重点在于分布式的治理。
Remoting:远程通讯,提供对多种NIO框架抽象封装,包括“同步转异步”和“请求-响应”模式的信息交换方式。
Cluster: 服务框架,提供基于接口方法 的透明远程过程调用,包括多协议支持,以及软负载均衡,失败容错,地址路由,动态配置等集群支持。
Registry: 服务注册,基于注册中心目录服务,使服务消费方能动态的查找服务提供方,使地址透明,使服务提供方可以平滑增加或减少机器。
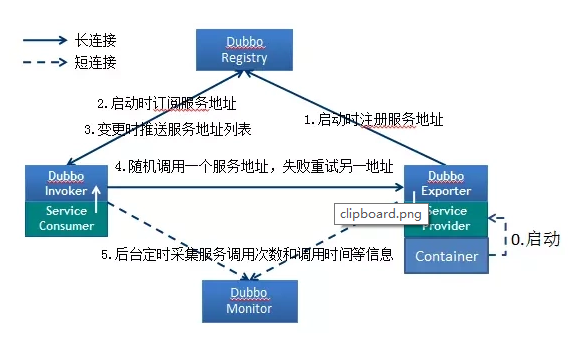
*Dubbo组件角色 *
调用关系:
服务容器 负责启动,加载,运行服务提供者 服务提供者在启动时,向注册中心注册 自己提供的服务。
服务消费者在启动时,向注册中心订阅 自己所需的服务。
注册中心 返回服务提供者地址列表 给消费者 ,如果有变更,注册中心将基于长连接推送变更数据给消费者。服务消费者,从提供者地址列表中,基于软负载均衡算法,选一台提供者进行调用,如果调用失败,再选另一台调用。
服务消费者和提供者,在内存中累计调用次数和调用时间,定时每分钟发送一次统计数据到监控中心Monitor。
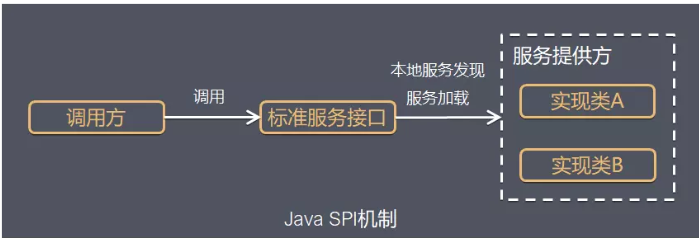
SPI(Service Provider Interfaces) 它是Java提供的一套用来被第三方实现或者扩展的API ,它可以用来启用框架扩展和替换组件。在JDK文档中,它这样解释道:
A service is a well-known set of interfaces and (usually abstract) classes. A service provider is a specific implementation of a service.
在面向对象的设计里面,模块之间推荐是基于接口编程,而不是对实现类进行硬编码,这样做也是为了模块设计的可拔插原则。为了在模块装配的时候不再程序里指明是那个实现,就需要一种服务发现的机制,jDK的SPI就是为某个接口寻找服务实现。
Java SPI实际上就是基于接口的编程+策略模式+配置文件 组合实现的动态加载机制。解耦
使用场景
数据库驱动加载接口实现类的加载
日志门面接口实现类加载
Spring
Dubbo
使用说明
当服务提供者提供了接口的一种具体实现后,在jar包的META-INF/service 目录下创建一个以”接口全限定名”为命名的文件,内容为实现类的全限定名。
接口实现类所在的jar包放在主程序的classpath中
主程序通过java.util.ServiceLoader动态加载实现模板,它通过扫描META-INF/services目录下的配置文件找到实现类的全限定名,把类加载到JVM
SPI的实现类必须携带一个不带参数的构造方法
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 110 111 112 113 114 115 116 117 118 119 120 121 122 123 124 125 126 127 128 129 130 131 132 133 134 135 136 137 138 139 140 141 142 143 144 145 146 147 148 149 150 151 152 153 154 155 156 157 158 159 160 161 162 163 164 165 166 167 168 169 170 171 172 173 174 175 176 177 178 179 180 181 182 183 184 185 186 187 188 189 190 191 192 193 194 195 196 197 198 199 200 201 202 203 204 205 206 207 208 209 210 211 212 213 214 215 216 217 218 219 220 221 222 223 224 225 226 227 228 229 230 231 232 233 234 235 236 237 238 239 240 241 242 243 244 245 246 247 248 249 250 251 252 253 254 255 256 257 258 259 260 261 262 263 264 265 266 267 268 269 270 271 272 273 274 275 276 277 278 public final class ServiceLoader <S > implements Iterable <S > private static final String PREFIX = "META-INF/services/" ; private final Class<S> service; private final ClassLoader loader; private final AccessControlContext acc; private LinkedHashMap<String,S> providers = new LinkedHashMap<>(); private LazyIterator lookupIterator; public void reload () providers.clear(); lookupIterator = new LazyIterator(service, loader); } private ServiceLoader (Class<S> svc, ClassLoader cl) service = Objects.requireNonNull(svc, "Service interface cannot be null" ); loader = (cl == null ) ? ClassLoader.getSystemClassLoader() : cl; acc = (System.getSecurityManager() != null ) ? AccessController.getContext() : null ; reload(); } private static void fail (Class<?> service, String msg, Throwable cause) throws ServiceConfigurationError { throw new ServiceConfigurationError(service.getName() + ": " + msg, cause); } private static void fail (Class<?> service, String msg) throws ServiceConfigurationError { throw new ServiceConfigurationError(service.getName() + ": " + msg); } private static void fail (Class<?> service, URL u, int line, String msg) throws ServiceConfigurationError { fail(service, u + ":" + line + ": " + msg); } private int parseLine (Class<?> service, URL u, BufferedReader r, int lc, List<String> names) throws IOException, ServiceConfigurationError { String ln = r.readLine(); if (ln == null ) { return -1 ; } int ci = ln.indexOf('#' ); if (ci >= 0 ) ln = ln.substring(0 , ci); ln = ln.trim(); int n = ln.length(); if (n != 0 ) { if ((ln.indexOf(' ' ) >= 0 ) || (ln.indexOf('\t' ) >= 0 )) fail(service, u, lc, "Illegal configuration-file syntax" ); int cp = ln.codePointAt(0 ); if (!Character.isJavaIdentifierStart(cp)) fail(service, u, lc, "Illegal provider-class name: " + ln); for (int i = Character.charCount(cp); i < n; i += Character.charCount(cp)) { cp = ln.codePointAt(i); if (!Character.isJavaIdentifierPart(cp) && (cp != '.' )) fail(service, u, lc, "Illegal provider-class name: " + ln); } if (!providers.containsKey(ln) && !names.contains(ln)) names.add(ln); } return lc + 1 ; } private Iterator<String> parse (Class<?> service, URL u) throws ServiceConfigurationError { InputStream in = null ; BufferedReader r = null ; ArrayList<String> names = new ArrayList<>(); try { in = u.openStream(); r = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(in, "utf-8" )); int lc = 1 ; while ((lc = parseLine(service, u, r, lc, names)) >= 0 ); } catch (IOException x) { fail(service, "Error reading configuration file" , x); } finally { try { if (r != null ) r.close(); if (in != null ) in.close(); } catch (IOException y) { fail(service, "Error closing configuration file" , y); } } return names.iterator(); } private class LazyIterator implements Iterator <S > { Class<S> service; ClassLoader loader; Enumeration<URL> configs = null ; Iterator<String> pending = null ; String nextName = null ; private LazyIterator (Class<S> service, ClassLoader loader) this .service = service; this .loader = loader; } private boolean hasNextService () if (nextName != null ) { return true ; } if (configs == null ) { try { String fullName = PREFIX + service.getName(); if (loader == null ) configs = ClassLoader.getSystemResources(fullName); else configs = loader.getResources(fullName); } catch (IOException x) { fail(service, "Error locating configuration files" , x); } } while ((pending == null ) || !pending.hasNext()) { if (!configs.hasMoreElements()) { return false ; } pending = parse(service, configs.nextElement()); } nextName = pending.next(); return true ; } private S nextService () if (!hasNextService()) throw new NoSuchElementException(); String cn = nextName; nextName = null ; Class<?> c = null ; try { c = Class.forName(cn, false , loader); } catch (ClassNotFoundException x) { fail(service, "Provider " + cn + " not found" ); } if (!service.isAssignableFrom(c)) { fail(service, "Provider " + cn + " not a subtype" ); } try { S p = service.cast(c.newInstance()); providers.put(cn, p); return p; } catch (Throwable x) { fail(service, "Provider " + cn + " could not be instantiated" , x); } throw new Error(); } public boolean hasNext () if (acc == null ) { return hasNextService(); } else { PrivilegedAction<Boolean> action = new PrivilegedAction<Boolean>() { public Boolean run () return hasNextService(); } }; return AccessController.doPrivileged(action, acc); } } public S next () if (acc == null ) { return nextService(); } else { PrivilegedAction<S> action = new PrivilegedAction<S>() { public S run () return nextService(); } }; return AccessController.doPrivileged(action, acc); } } public void remove () throw new UnsupportedOperationException(); } } public Iterator<S> iterator () return new Iterator<S>() { Iterator<Map.Entry<String,S>> knownProviders = providers.entrySet().iterator(); public boolean hasNext () if (knownProviders.hasNext()) return true ; return lookupIterator.hasNext(); } public S next () if (knownProviders.hasNext()) return knownProviders.next().getValue(); return lookupIterator.next(); } public void remove () throw new UnsupportedOperationException(); } }; } public static <S> ServiceLoader<S> load (Class<S> service, ClassLoader loader) { return new ServiceLoader<>(service, loader); } public static <S> ServiceLoader<S> load (Class<S> service) { ClassLoader cl = Thread.currentThread().getContextClassLoader(); return ServiceLoader.load(service, cl); } public static <S> ServiceLoader<S> loadInstalled (Class<S> service) { ClassLoader cl = ClassLoader.getSystemClassLoader(); ClassLoader prev = null ; while (cl != null ) { prev = cl; cl = cl.getParent(); } return ServiceLoader.load(service, prev); } public String toString () return "java.util.ServiceLoader[" + service.getName() + "]" ; } }
ServiceLoader不是实例化以后,就去读取文件的具体实现。而是等到使用迭代器去遍历的时候,才会加载对应的配置文件去解析,调用hasNext方法时就去加载配置文件进行解析,调用Next方法的时候进行实例化并缓存。
优点
缺点
Dubbo的SPI机制
扩展点必须是Interface类型,必须被@SPI注释
配置文件存储在META-INF/services/ 和META-INF/dubbo/ 和META-INF/dubbo/internal ,这些路径下定义的文件名为扩展点接口的全类名,文件中以键值对的形式配置扩展点的扩展实现,这与JDk SPI的存储形式有很大不同,所以在Dubbo中无法直接使用ServiceLoader, 而是使用ExtensionLoader,可用于载入Dubbo中的各种可配置组件,比如动态代理方式(ProxyFactory)、负载均衡策略(LoadBalance)、RCP协议(Protocol)、拦截器(Filter)、容器类型(Container)、集群方式(Cluster)和注册中心类型等。META-INF/dubbo/internal/com.alibaba.dubbo.common.extension.ExtensionFactory 中定义的扩展 : 1 2 3 adaptive = com.alibaba.dubbo.common.extension.factory.AdaptiveExtensionFactory spi = com.alibaba.dubbo.common.extension.factory.SpiExtensionFactory spring = com.alibaba.dubbo.config.spring.extension.SpringExtensionFactor
在标识扩展点时会用到这几个标识,@SPI 、 @Adaptive、 @Activate
@SPI (注解在类上):该注解标识了接口是一个扩展点,属性value用来指定默认适配扩展点的名称。传入的URL类型的参数或者内部含有获取URL方法的参数 ,从URL中获取到要使用的扩展类的名称,再去根据名称加载对应的扩展实例,用这个扩展实例对象调用相同的方法。如果运行时没有适配到运行的扩展实例,那么就使用@SPI注解缺省指定的扩展。通过这种方式就实现了运行时去适配到对应的扩展。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 @SPI ("netty" )public interface Transporter @Adaptive ({Constants.SERVER_KEY, Constants.TRANSPORTER_KEY}) Server bind (URL url, ChannelHandler handler) throws RemotingException ; @Adaptive ({Constants.CLIENT_KEY, Constants.TRANSPORTER_KEY}) Client connect (URL url, ChannelHandler handler) throws RemotingException ; }
ExtensionLoader会通过createAdaptiveExtensionClassCode方法动态生成一个Transporter$Adaptive类 ,生成的代码如下:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 package com.alibaba.dubbo.remoting;import com.alibaba.dubbo.common.extension.ExtensionLoader;public class Transporter $Adaptive implements com .alibaba .dubbo .remoting .Transporter public com.alibaba.dubbo.remoting.Client connect (com.alibaba.dubbo.common.URL arg0, com.alibaba.dubbo.remoting.ChannelHandler arg1) throws com.alibaba.dubbo.remoting.RemotingException { if (arg0 == null ) throw new IllegalArgumentException("url == null" ); com.alibaba.dubbo.common.URL url = arg0; String extName = url.getParameter("client" , url.getParameter("transporter" , "netty" )); if (extName == null ) throw new IllegalStateException("Fail to get extension(com.alibaba.dubbo.remoting.Transporter) name from url(" + url.toString() + ") use keys([client, transporter])" ); com.alibaba.dubbo.remoting.Transporter extension = (com.alibaba.dubbo.remoting.Transporter)ExtensionLoader.getExtensionLoader (com.alibaba.dubbo.remoting.Transporter.class).getExtension(extName); return extension.connect(arg0, arg1); } public com.alibaba.dubbo.remoting.Server bind (com.alibaba.dubbo.common.URL arg0, com.alibaba.dubbo.remoting.ChannelHandler arg1) throws com.alibaba.dubbo.remoting.RemotingException { if (arg0 == null ) throw new IllegalArgumentException("url == null" ); com.alibaba.dubbo.common.URL url = arg0; String extName = url.getParameter("server" , url.getParameter("transporter" , "netty" )); if (extName == null ) throw new IllegalStateException("Fail to get extension(com.alibaba.dubbo.remoting.Transporter) name from url(" + url.toString() + ") use keys([server, transporter])" ); com.alibaba.dubbo.remoting.Transporter extension = (com.alibaba.dubbo.remoting.Transporter)ExtensionLoader.getExtensionLoader (com.alibaba.dubbo.remoting.Transporter.class).getExtension(extName); return extension.bind(arg0, arg1); } }
这些代码都是模板代码,最核心的代码只有一行,是为了去获取指定名称的扩展实例对象。
扩展加载器 ExtensionLoader 它控制着所有扩展点的初始化、加载扩展的过程。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 private static final Logger logger = LoggerFactory.getLogger(ExtensionLoader.class); private static final String SERVICES_DIRECTORY = "META-INF/services/" ; private static final String DUBBO_DIRECTORY = "META-INF/dubbo/" ; private static final String DUBBO_INTERNAL_DIRECTORY = DUBBO_DIRECTORY + "internal/" ; private static final Pattern NAME_SEPARATOR = Pattern.compile("\\s*[,]+\\s*" ); private static final ConcurrentMap<Class<?>, ExtensionLoader<?>> EXTENSION_LOADERS = new ConcurrentHashMap<Class<?>, ExtensionLoader<?>>(); private static final ConcurrentMap<Class<?>, Object> EXTENSION_INSTANCES = new ConcurrentHashMap<Class<?>, Object>(); private final Class<?> type; private final ExtensionFactory objectFactory; private final ConcurrentMap<Class<?>, String> cachedNames = new ConcurrentHashMap<Class<?>, String>(); private final Holder<Map<String, Class<?>>> cachedClasses = new Holder<Map<String, Class<?>>>(); private final Map<String, Activate> cachedActivates = new ConcurrentHashMap<String, Activate>(); private final ConcurrentMap<String, Holder<Object>> cachedInstances = new ConcurrentHashMap<String, Holder<Object>>(); private final Holder<Object> cachedAdaptiveInstance = new Holder<Object>(); private volatile Class<?> cachedAdaptiveClass = null ; private String cachedDefaultName; private volatile Throwable createAdaptiveInstanceError; private Set<Class<?>> cachedWrapperClasses; private Map<String, IllegalStateException> exceptions = new ConcurrentHashMap<String, IllegalStateException>();
ExtensionLoader没有提供public的构造方法,有一个私有的构造方法,获取ExtensionLoader实例的工厂方法,但是提供了一个public static的getExtensionLoader。其public成员方法中有三个比较重要的方法:
1 2 3 4 private ExtensionLoader (Class<?> type) this .type = type; objectFactory = (type == ExtensionFactory.class ? null : ExtensionLoader.getExtensionLoader(ExtensionFactory.class).getAdaptiveExtension()); }
1 2 3 4 5 @SPI public interface ExtensionFactory <T> T getExtension (Class<T> type, String name) ; }
从上可以看出ExtensionFactory也是一个扩展点,有两个实现类:SpiExtensionFactory和AdaptiveExtensionFactory,实际上还有一个SpringExtensionFactory,不同的实现类可以用不同的方式来完成扩展点实现的加载。如果要加载的扩展点类型是ExtensionFactory,那么object设置为null。ExtensionFactory实现中,AdaptiveExtensionFactory被@Adaptive注解注释,也就是说它是ExtensionFactory对应的自适应扩展实现(每个扩展点最多只能有一个自适应实现,如果所有实现中没有被@Adaptive注释的,那么dubbo会动态生成一个自适应实现类)
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 @Adaptive public class AdaptiveExtensionFactory implements ExtensionFactory private final List<ExtensionFactory> factories; public AdaptiveExtensionFactory () ExtensionLoader<ExtensionFactory> loader = ExtensionLoader.getExtensionLoader(ExtensionFactory.class); List<ExtensionFactory> list = new ArrayList<ExtensionFactory>(); for (String name : loader.getSupportedExtensions()) { list.add(loader.getExtension(name)); } factories = Collections.unmodifiableList(list); } @Override public <T> T getExtension (Class<T> type, String name) { for (ExtensionFactory factory : factories) { T extension = factory.getExtension(type, name); if (extension != null ) { return extension; } } return null ; } }
上述代码中调用到了ExtensionLoader类中的getSupportedExtensions方法,所以接下来再分析ExtensionLoader类。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 public static <T> ExtensionLoader<T> getExtensionLoader (Class<T> type) { if (type == null ) throw new IllegalArgumentException("Extension type == null" ); if (!type.isInterface()) { throw new IllegalArgumentException("Extension type(" + type + ") is not interface!" ); } if (!withExtensionAnnotation(type)) { throw new IllegalArgumentException("Extension type(" + type + ") is not extension, because WITHOUT @" + SPI.class.getSimpleName() + " Annotation!" ); } ExtensionLoader<T> loader = (ExtensionLoader<T>) EXTENSION_LOADERS.get(type); if (loader == null ) { EXTENSION_LOADERS.putIfAbsent(type, new ExtensionLoader<T>(type)); loader = (ExtensionLoader<T>) EXTENSION_LOADERS.get(type); } return loader; }
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 public T getAdaptiveExtension () Object instance = cachedAdaptiveInstance.get(); if (instance == null ) { if (createAdaptiveInstanceError == null ) { synchronized (cachedAdaptiveInstance) { instance = cachedAdaptiveInstance.get(); if (instance == null ) { try { instance = createAdaptiveExtension(); cachedAdaptiveInstance.set(instance); } catch (Throwable t) { createAdaptiveInstanceError = t; throw new IllegalStateException("fail to create adaptive instance: " + t.toString(), t); } } } } else { throw new IllegalStateException("fail to create adaptive instance: " + createAdaptiveInstanceError.toString(), createAdaptiveInstanceError); } } return (T) instance; }
在ExtensionLoader的私有构造方法中可以看出,在选择ExtensionFactory的时候,并不是用getExtension(name)来获取某个具体的实现类,而是调用getAdaptiveExtension来获取一个自适应的实现。createAdaptiveExtension 方法来创建新的adaptiveInstance并且缓存起来,也就是说对于某个扩展点,每次调用ExtensionLoader.getAdaptiveExtension获取到的都是同一个实例。
首先会获取到该扩展点类的注解中的值,获取默认值,然后从特定目录下读取配置文件中的信息,loadClass ,将有关类放到extensionClasses变量中
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 110 111 112 113 114 115 116 117 118 119 120 121 122 123 124 125 126 127 128 129 130 131 132 133 134 135 136 137 138 139 140 141 142 143 144 145 146 147 148 149 150 151 152 153 154 155 156 157 158 159 160 161 162 163 164 165 166 167 168 169 170 171 172 173 174 private T createAdaptiveExtension () try { return injectExtension((T) getAdaptiveExtensionClass().newInstance()); } catch (Exception e) { throw new IllegalStateException("Can not create adaptive extension " + type + ", cause: " + e.getMessage(), e); } } private Class<?> getAdaptiveExtensionClass() { getExtensionClasses(); if (cachedAdaptiveClass != null ) { return cachedAdaptiveClass; } return cachedAdaptiveClass = createAdaptiveExtensionClass(); } private Map<String, Class<?>> getExtensionClasses() { Map<String, Class<?>> classes = cachedClasses.get(); if (classes == null ) { synchronized (cachedClasses) { classes = cachedClasses.get(); if (classes == null ) { classes = loadExtensionClasses(); cachedClasses.set(classes); } } } return classes; } private Map<String, Class<?>> loadExtensionClasses() { final SPI defaultAnnotation = type.getAnnotation(SPI.class); if (defaultAnnotation != null ) { String value = defaultAnnotation.value(); if ((value = value.trim()).length() > 0 ) { String[] names = NAME_SEPARATOR.split(value); if (names.length > 1 ) { throw new IllegalStateException("more than 1 default extension name on extension " + type.getName() + ": " + Arrays.toString(names)); } if (names.length == 1 ) cachedDefaultName = names[0 ]; } } Map<String, Class<?>> extensionClasses = new HashMap<String, Class<?>>(); loadDirectory(extensionClasses, DUBBO_INTERNAL_DIRECTORY); loadDirectory(extensionClasses, DUBBO_DIRECTORY); loadDirectory(extensionClasses, SERVICES_DIRECTORY); return extensionClasses; } private void loadDirectory (Map<String, Class<?>> extensionClasses, String dir) String fileName = dir + type.getName(); try { Enumeration<java.net.URL> urls; ClassLoader classLoader = findClassLoader(); if (classLoader != null ) { urls = classLoader.getResources(fileName); } else { urls = ClassLoader.getSystemResources(fileName); } if (urls != null ) { while (urls.hasMoreElements()) { java.net.URL resourceURL = urls.nextElement(); loadResource(extensionClasses, classLoader, resourceURL); } } } catch (Throwable t) { logger.error("Exception when load extension class(interface: " + type + ", description file: " + fileName + ")." , t); } } private void loadResource (Map<String, Class<?>> extensionClasses, ClassLoader classLoader, java.net.URL resourceURL) try { BufferedReader reader = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(resourceURL.openStream(), "utf-8" )); try { String line; while ((line = reader.readLine()) != null ) { final int ci = line.indexOf('#' ); if (ci >= 0 ) line = line.substring(0 , ci); line = line.trim(); if (line.length() > 0 ) { try { String name = null ; int i = line.indexOf('=' ); if (i > 0 ) { name = line.substring(0 , i).trim(); line = line.substring(i + 1 ).trim(); } if (line.length() > 0 ) { loadClass(extensionClasses, resourceURL, Class.forName(line, true , classLoader), name); } } catch (Throwable t) { IllegalStateException e = new IllegalStateException("Failed to load extension class(interface: " + type + ", class line: " + line + ") in " + resourceURL + ", cause: " + t.getMessage(), t); exceptions.put(line, e); } } } } finally { reader.close(); } } catch (Throwable t) { logger.error("Exception when load extension class(interface: " + type + ", class file: " + resourceURL + ") in " + resourceURL, t); } } private void loadClass (Map<String, Class<?>> extensionClasses, java.net.URL resourceURL, Class<?> clazz, String name) throws NoSuchMethodException if (!type.isAssignableFrom(clazz)) { throw new IllegalStateException("Error when load extension class(interface: " + type + ", class line: " + clazz.getName() + "), class " + clazz.getName() + "is not subtype of interface." ); } if (clazz.isAnnotationPresent(Adaptive.class)) { if (cachedAdaptiveClass == null ) { cachedAdaptiveClass = clazz; } else if (!cachedAdaptiveClass.equals(clazz)) { throw new IllegalStateException("More than 1 adaptive class found: " + cachedAdaptiveClass.getClass().getName() + ", " + clazz.getClass().getName()); } } else if (isWrapperClass(clazz)) { Set<Class<?>> wrappers = cachedWrapperClasses; if (wrappers == null ) { cachedWrapperClasses = new ConcurrentHashSet<Class<?>>(); wrappers = cachedWrapperClasses; } wrappers.add(clazz); } else { clazz.getConstructor(); if (name == null || name.length() == 0 ) { name = findAnnotationName(clazz); if (name.length() == 0 ) { throw new IllegalStateException("No such extension name for the class " + clazz.getName() + " in the config " + resourceURL); } } String[] names = NAME_SEPARATOR.split(name); if (names != null && names.length > 0 ) { Activate activate = clazz.getAnnotation(Activate.class); if (activate != null ) { cachedActivates.put(names[0 ], activate); } for (String n : names) { if (!cachedNames.containsKey(clazz)) { cachedNames.put(clazz, n); } Class<?> c = extensionClasses.get(n); if (c == null ) { extensionClasses.put(n, clazz); } else if (c != clazz) { throw new IllegalStateException("Duplicate extension " + type.getName() + " name " + n + " on " + c.getName() + " and " + clazz.getName()); } } } } }
上述代码完成了自适应扩展点类型的实现和实例化,下面方法是扩展点自动注入的实现,它会获取处理当前实例的所有set方法对应的参数类型和property名称,根据这两个条件从ExtensionFactory中查询,如果有返回扩展点实例,那么就进行注入操作。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 private T injectExtension (T instance) try { if (objectFactory != null ) { for (Method method : instance.getClass().getMethods()) { if (method.getName().startsWith("set" ) && method.getParameterTypes().length == 1 && Modifier.isPublic(method.getModifiers())) { if (method.getAnnotation(DisableInject.class) != null ) { continue ; } Class<?> pt = method.getParameterTypes()[0 ]; try { String property = method.getName().length() > 3 ? method.getName().substring(3 , 4 ).toLowerCase() + method.getName().substring(4 ) : "" ; Object object = objectFactory.getExtension(pt, property); if (object != null ) { method.invoke(instance, object); } } catch (Exception e) { logger.error("fail to inject via method " + method.getName() + " of interface " + type.getName() + ": " + e.getMessage(), e); } } } } } catch (Exception e) { logger.error(e.getMessage(), e); } return instance; }
文章参考:dubbo源码一:ExtensionLoader及获取适配类过程解析 Dubbo扩展点加载机制 - ExtensionLoader 【Dubbo】Adaptive