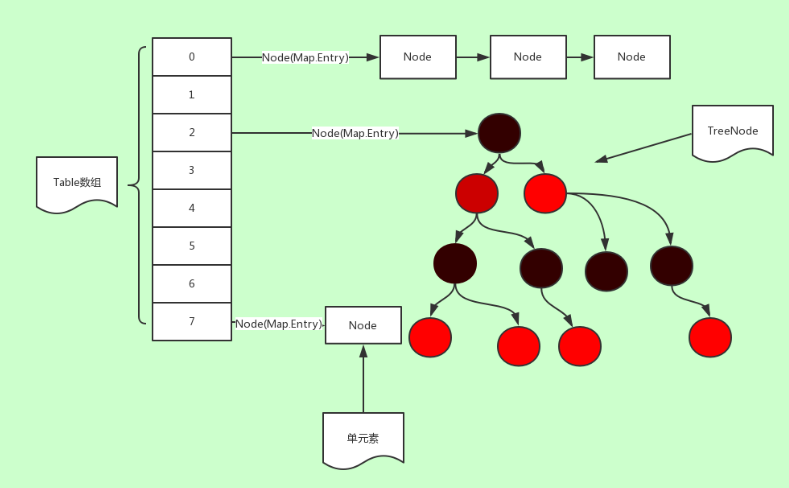
hashMap是一个常用的集合类,用来存放多组键值对,内部的数据结构在jdk1.6时是数组加链表,但到了jdk1.8时额外添加了红黑树,当某一链表长度超过某个值时会转化为红黑树。
HashMap1.6与1.8的区别 hashMap是一个常用的集合类,用来存放多组键值对,内部的数据结构在jdk1.6时是数组加链表,但到了jdk1.8时额外添加了红黑树,当某一链表长度超过某个值时会转化为红黑树。
HashMap 属性变量解释 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 #数组的初始化容量-数值必须时2的幂 static final int DEFAULT_INITIAL_CAPACITY = 1 << 4 ;#最大容量,可以使用一个带参数的构造函数来隐式的改变容量大小,但必须时2的幂且小于等于1<<30 static final int MAXIMUM_CAPACITY = 1 << 30 ;#负载因子初始值 static final float DEFAULT_LOAD_FACTOR = 0.75f ;#使用树(而不是列表)来设置bin计数阈值。当向至少具有这么多节点的bin添加元素时,bin将转换为树。该值必须大于#2,并且应该至少为8,以便与删除树时关于转换回普通桶的假设相匹配收缩。 static final int TREEIFY_THRESHOLD = 8 ;#当桶(bucket)上的结点数小于该值是应当树转链表 static final int UNTREEIFY_THRESHOLD = 6 ;#桶中结构转化为红黑树时对应的table的最小值 static final int MIN_TREEIFY_CAPACITY = 64 ;#tables数组,在必要时会重新调整大小,但长度总是2的幂 transient Node<K,V>[] table;#保存缓存的entrySet()。注意,使用了AbstractMap字段用于keySet()和values()。 transient Set<Map.Entry<K,V>> entrySet;#在该map中映射的key-value对数量 transient int size;#这个HashMap在结构上被修改的次数结构修改是指改变HashMap中映射的数量或修改其内部结构的次数(例如,#rehash)。此字段用于使HashMap集合视图上的迭代器快速失效。(见ConcurrentModificationException)。 transient int modCount;#要下一次调整大小的临界值(capacity * load factor) int threshold;#哈希表的加载因子 final float loadFactor;
源码中定义了四个构造函数,可以自定义容量和负载因子,也支持将定义好的Map作为参数,进行转化。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 public HashMap (int initialCapacity, float loadFactor) public HashMap (int initialCapacity) public HashMap () public HashMap (Map<? extends K, ? extends V> m)
HashMap中每个节点元素都是以node的类型,定义如下:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 static class Node <K ,V > implements Map .Entry <K ,V > final int hash; final K key; V value; #连接的下一个节点 Node<K,V> next; Node(int hash, K key, V value, Node<K,V> next) { this .hash = hash; this .key = key; this .value = value; this .next = next; } #计算hash值,会判断key是否为空, static final int hash (Object key) int h; return (key == null ) ? 0 : (h = key.hashCode()) ^ (h >>> 16 ); } }
HashMap添加数据 putval 在hashMap中添加新数据时会调用putVal()方法,它会根据key计算出hash值,然后通过计算 tab[i = (n - 1) & hash]
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 final V putVal (int hash, K key, V value, boolean onlyIfAbsent, boolean evict) Node<K,V>[] tab; Node<K,V> p; int n, i; #如果表为空,则对表进行初始化 if ((tab = table) == null || (n = tab.length) == 0 ) n = (tab = resize()).length; #如果计算的位置为空,没有结点,就直接插入,否则就进入该位置的链表逐个查询 if ((p = tab[i = (n - 1 ) & hash]) == null ) tab[i] = newNode(hash, key, value, null ); else { Node<K,V> e; K k; #通过hash值和key值进行判断,得出插入位置 if (p.hash == hash && ((k = p.key) == key || (key != null && key.equals(k)))) e = p; else if (p instanceof TreeNode) e = ((TreeNode<K,V>)p).putTreeVal(this , tab, hash, key, value); else { for (int binCount = 0 ; ; ++binCount) { #当插入的位置为该链表的尾结点时,则直接插入,当超出阈值时,则转化为红黑树 if ((e = p.next) == null ) { p.next = newNode(hash, key, value, null ); if (binCount >= TREEIFY_THRESHOLD - 1 ) treeifyBin(tab, hash); break ; } if (e.hash == hash && ((k = e.key) == key || (key != null && key.equals(k)))) break ; p = e; } } #当该位置存在旧值时,修改赋值,并返回旧址 if (e != null ) { V oldValue = e.value; if (!onlyIfAbsent || oldValue == null ) e.value = value; afterNodeAccess(e); return oldValue; } } #增加修改次数 ++modCount; #当大小超过阈值时,进行扩展 if (++size > threshold) resize(); afterNodeInsertion(evict); return null ; }
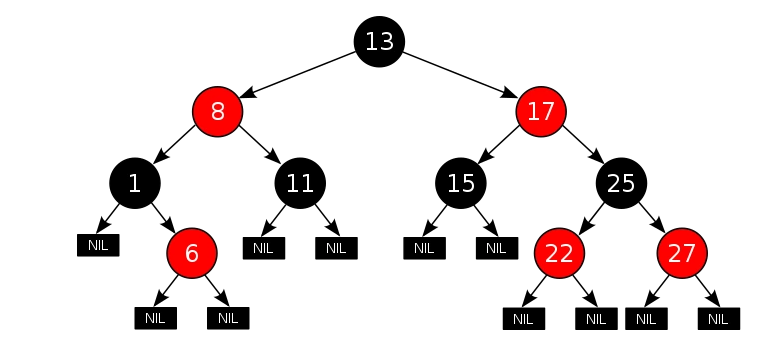
红黑树
为了更好的理解红黑树在HashMap中的运用,我先简单的介绍红黑树的定义及特点。红黑树特性
结点是红色或黑色
根节点永远是黑色
叶子结点(NIL结点)都是黑色
红色结点的两个直接孩子结点都是黑色
任一结点到其每个叶子的所有路径都包含相同数目的黑色结点
红黑树结构
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 static final class TreeNode<K,V> extends LinkedHashMap.Entry<K,V> { #父结点 TreeNode<K,V> parent; // red-black tree links #左结点 TreeNode<K,V> left; #右结点 TreeNode<K,V> right; #上结点 TreeNode<K,V> prev; // needed to unlink next upon deletion #标注该结点是否为红色 boolean red; TreeNode(int hash, K key, V val, Node<K,V> next) { super(hash, key, val, next); }
-将链表转化为红黑树时会调用treeifyBin方法
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 final void treeifyBin (Node<K,V>[] tab, int hash) int n, index; Node<K,V> e; #当长度小于阈值时会进行扩容处理 if (tab == null || (n = tab.length) < MIN_TREEIFY_CAPACITY) resize(); #确定要转化为红黑树的链表的位置 else if ((e = tab[index = (n - 1 ) & hash]) != null ) { TreeNode<K,V> hd = null , tl = null ; do { #将Node类型转化为TreeNode类型 TreeNode<K,V> p = replacementTreeNode(e, null ); #记录头结点 if (tl == null ) hd = p; #双向链表 else { p.prev = tl; tl.next = p; } #记录上一个结点,以方便记录prev tl = p; } while ((e = e.next) != null ); if ((tab[index] = hd) != null ) #将树形链表转化为红黑树 hd.treeify(tab); } }
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 static final class TreeNode <K ,V > extends LinkedHashMap .Entry <K ,V > TreeNode<K,V> parent; TreeNode<K,V> left; TreeNode<K,V> right; TreeNode<K,V> prev; boolean red; final void treeify (Node<K,V>[] tab) TreeNode<K,V> root = null ; #从该结点进行遍历 for (TreeNode<K,V> x = this , next; x != null ; x = next) { #记录当前结点的下一个结点 next = (TreeNode<K,V>)x.next; x.left = x.right = null ; if (root == null ) { x.parent = null ; #当为根节点时,为黑色 x.red = false ; root = x; } else { K k = x.key; int h = x.hash; Class<?> kc = null ; for (TreeNode<K,V> p = root;;) { int dir, ph; K pk = p.key; #当前的结点比红黑树一结点小时,向左转 if ((ph = p.hash) > h) dir = -1 ; #大于时,向右转 else if (ph < h) dir = 1 ; #当hash值相等时 else if ((kc == null && (kc = comparableClassFor(k)) == null ) || (dir = compareComparables(kc, k, pk)) == 0 ) dir = tieBreakOrder(k, pk); #保留当前结点 TreeNode<K,V> xp = p; #如果dir 小于等于0 : 当前链表节点一定放置在当前树节点的左侧,但不一定是该树节点的左孩子,也可能是左孩子的右孩子 或者 更深层次的节点。 如果dir 大于0 : 当前链表节点一定放置在当前树节点的右侧,但不一定是该树节点的右孩子,也可能是右孩子的左孩子 或者 更深层次的节点。 如果当前树节点不是叶子节点,那么最终会以当前树节点的左孩子或者右孩子 为 起始节点 再从上处开始 重新寻找自己(当前链表节点)的位置 如果当前树节点就是叶子节点,那么根据dir的值,就可以把当前链表节点挂载到当前树节点的左或者右侧了。 挂载之后,还需要重新把树进行平衡。平衡之后,就可以针对下一个链表节点进行处理了。 if ((p = (dir <= 0 ) ? p.left : p.right) == null ) { x.parent = xp; if (dir <= 0 ) xp.left = x; else xp.right = x; root = balanceInsertion(root, x); break ; } } } } #Ensures that the given root is the first node of its bin. moveRootToFront(tab, root); }
HashMap的缺点
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 void resize (int newCapacity) Entry[] oldTable = table; int oldCapacity = oldTable.length; if (oldCapacity == MAXIMUM_CAPACITY) { threshold = Integer.MAX_VALUE; return ; } #创建新的数组 Entry[] newTable = new Entry[newCapacity]; transfer(newTable); table = newTable; threshold = (int )(newCapacity * loadFactor); }
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 void transfer (Entry[] newTable) Entry[] src = table; int newCapacity = newTable.length; for (int j = 0 ; j<src.length; j++) { Entry<K,V> e = src[j]; if (e != null ) { src[j] = null ; do { #采用头插法进行链表的重新构建连接 Entry<K,V> next = e.next; int i = indexFor(e.hash, newCapacity); e.next = newTable[i]; newTable[i] = e; e = next; } while (e != null ); } } }
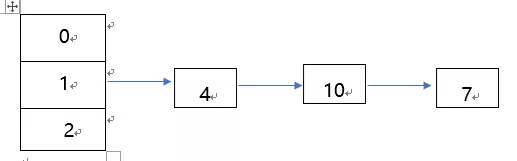
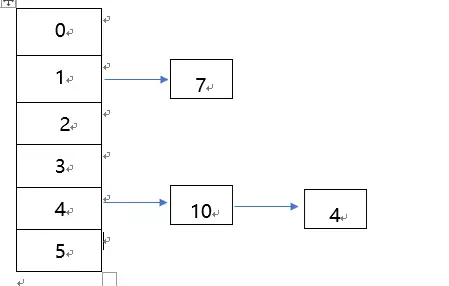
假设初始化一个数组,长度为3,有3个数,为4,10, 7,根据mod操作,都在tab[1]上,发生冲突,构建链表。
[^1]然后进行扩容resize()操作,tab数组大小扩展为原来的两倍,在单线程下操作会变成下面的结构,没有发生异常,因为采用头插法,所有链表中数据的相对顺序会发生颠倒,但在高并发情况下可能会发生异常。
现在假设有两个线程在执行resize()操作,线程1执行到Entry<K,V> next = e.next e.next = newTable[i]; 位置时被挂起,此时,线程1记录的e 为4,next 为10,然后执行线程2的操作,顺利完成,结果和上图一致。此时,再继续执行线程1剩余的操作newTable[i] = e; e = next ; 此时e变成了10,而线程2已修改10的next是4,就形成了死循环。
note: &操作
在下方 代码中有一步是e.hash & (newCap - 1) , 该方法相当与取余操作,但有限制,只有当b为2的n次方时才有效, a % b = a & (b -1) (b =[2^n])1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 final Node<K,V>[] resize() { Node<K,V>[] oldTab = table; int oldCap = (oldTab == null ) ? 0 : oldTab.length; int oldThr = threshold; int newCap, newThr = 0 ; if (oldCap > 0 ) { if (oldCap >= MAXIMUM_CAPACITY) { threshold = Integer.MAX_VALUE; return oldTab; } else if ((newCap = oldCap << 1 ) < MAXIMUM_CAPACITY && oldCap >= DEFAULT_INITIAL_CAPACITY) # 修改新的临界值为原来的两倍,进行移位操作速度会更快些,算是个小技巧 newThr = oldThr << 1 ; } else if (oldThr > 0 ) newCap = oldThr; else { newCap = DEFAULT_INITIAL_CAPACITY; newThr = (int )(DEFAULT_LOAD_FACTOR * DEFAULT_INITIAL_CAPACITY); } if (newThr == 0 ) { float ft = (float )newCap * loadFactor; newThr = (newCap < MAXIMUM_CAPACITY && ft < (float )MAXIMUM_CAPACITY ? (int )ft : Integer.MAX_VALUE); } threshold = newThr; @SuppressWarnings ({"rawtypes" ,"unchecked" }) #创建新的数组 Node<K,V>[] newTab = (Node<K,V>[])new Node[newCap]; table = newTab; if (oldTab != null ) { for (int j = 0 ; j < oldCap; ++j) { Node<K,V> e; if ((e = oldTab[j]) != null ) { oldTab[j] = null ; #该位置下只有一个元素 if (e.next == null ) newTab[e.hash & (newCap - 1 )] = e; #如果该节点是树结构 else if (e instanceof TreeNode) ((TreeNode<K,V>)e).split(this , newTab, j, oldCap); else { #定义了两个链表,low和high Node<K,V> loHead = null , loTail = null ; Node<K,V> hiHead = null , hiTail = null ; Node<K,V> next; do { next = e.next; #判断该元素是放到原索引处还是新索引处 if ((e.hash & oldCap) == 0 ) { #放到原索引处建立新链表 #jdk1.8之前是头插法,现在改为了尾插法 if (loTail == null ) loHead = e; else loTail.next = e; loTail = e; } #放到新索引处建立建立新链表 else { if (hiTail == null ) hiHead = e; else hiTail.next = e; hiTail = e; } } while ((e = next) != null ); if (loTail != null ) { loTail.next = null ; newTab[j] = loHead; } if (hiTail != null ) { hiTail.next = null ; newTab[j + oldCap] = hiHead; } } } } } return newTab; }
但在jdk1.8中HashMap中会存在了数据丢失问题,在多线程情况下建议使用ConcurrentHashMap
##HashMap为什么选择桶中个数超过8个时才会转化为红黑树
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 Because TreeNodes are about twice the size of regular nodes, we use them only when bins contain enough nodes to warrant use (see TREEIFY_THRESHOLD). And when they become too small (due to removal or resizing) they are converted back to plain bins. In usages with well-distributed user hashCodes, tree bins are rarely used. Ideally, under random hashCodes, the frequency of nodes in bins follows a Poisson distribution
在理想状态下,通过hashmap算法所有的节点几乎都遵循泊松分布,一个bin中的链表长度超过8的概率为0.00000006,几率很小,而转化为红黑树也在很少情况下,在该长度下也能更好的发挥树的优势。
才疏学浅,有不足地方希望能够及时提出,互相学习https://www.jianshu.com/u/a8d49bf62c45